As a developer, we all are using some kind of source control provider to maintain versions of our source code. But another aspects of source control to is to make sure that code committed in source code repositories are perfect and it will not break the build of particular software. That’s why Continuous integration is very much popular this days.
What is Continuous Integration:
Continuous integration (CI) is the practice, in software engineering, of merging all developer working copies with a shared mainline several times a day. It was first named and proposed by Grady Booch in his method, who did not advocate integrating several times a day.In simple words, when developers checks in or commit code to source code repository a build of software will automatically triggers to check whether current check-in/commit of code breaks code or not.
In this post we will learn how we are going to use visualstudio.com and TFS for continuous integration of our sample application.
What is VisualStudio.com:
Followings are some of features of visualstudio.com.
- It provides complete ALM applications online you don’t have to need to setup an infrastructure for that.
- It supports Git(Distributed) and TFVS(centralized) source control.
- It supports continuous integration so it creates build server when they are required and bring down when its not required.
- It supports latest project management workflows like Agile.
- It supports team collaborations, which facilities real-time collaboration between teams.
- It’s free for 5 users.
http://www.visualstudio.com/products/what-is-visual-studio-online-vs
Setting up code repository with visualstudio.com:

Click on new to create new project. It will load dialog for create new project.
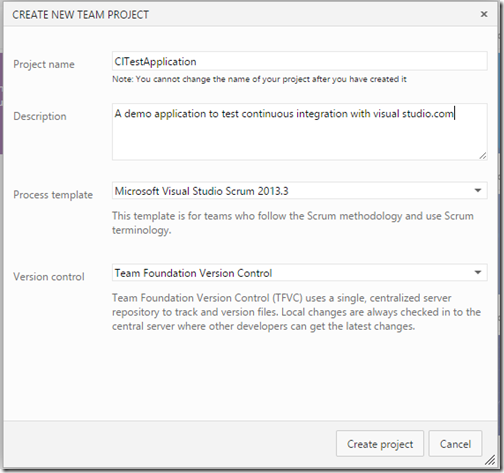
It will ask for your project name, description related to project and it will ask to choose your template and version controlling system. Here I have selected Team foundation version control but it will also support Git also. Clicking on “Create project” will create new project. Once project is created you can navigate to that project from dashboard.
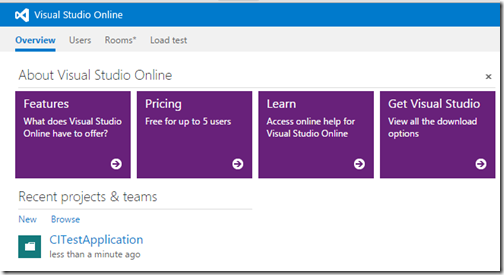
Clicking on that project will present you a dashboard of selected project.

On right side of dashboard there is a link called “Open in visual studio”.

Once you click on it. It will launch visual studio from your desktop. In visual studio go to team explorer it will ask you configure your work space.
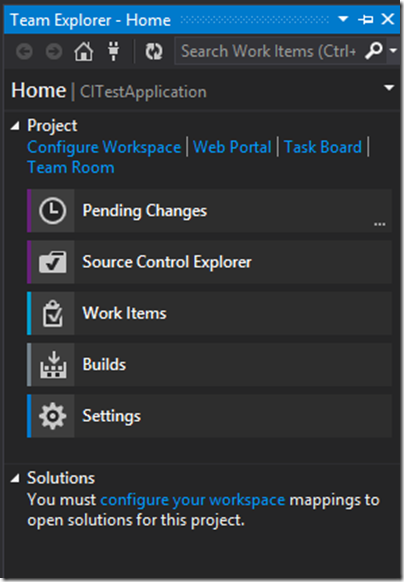
Click on configure work space. It will ask to set map your work space with location.

Then click on Map and get. Once mapping is done you can add the solution to project. From Team explorer go to solution part and click on new solution part.
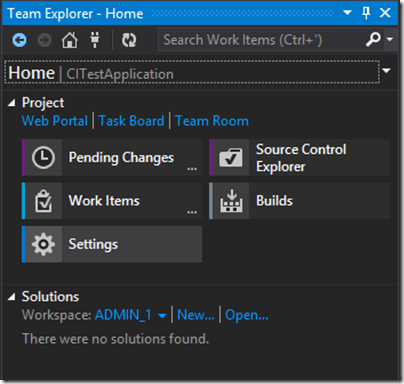
Here I’m going to use ASP.NET MVC sample application so I will add an ASP.NET MVC project to solution and team explorer project.

Created ASP.NET application and selected MVC as below.

Now it’s time to build definition so go to team explorer and click on build.

It will load build section.

Click on new Build Definition it will load build definition dialog. In General tab of build definition you need to make sure it is enabled.

Now go to Trigger part where you need to check continuous radio button. Which will trigger build on each commit.

Now you close the build dialog it will save the current build definition. And you see it in all build definition in team explorer.

Now to test the continuous integration, go to pending changes in team explorer and check in the code.

Now as soon as you check in it will queue a build in build section.

You can see that in visualstudio.com also.

As soon as it completes building solution, It will update the status at both places.

Same for visualstudio.com.

That’s it. It is very easy to setup continuous integration with visualstudio.com. So what you are waiting for go and start using it. Stay tuned for more.


Good Post , Very Useful
ReplyDeleteThanks
DeleteGood blog, great initiative. Please add test automation framework!
ReplyDeleteThanks Shital!
Delete